The Clinical Efficiency of 980 nm Diode Laser in Management of Labial Mucocele: Case Report
Main Article Content
Abstract
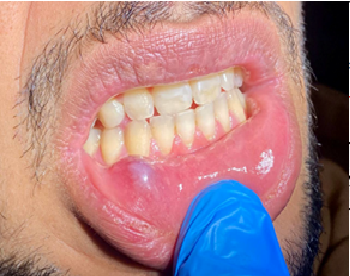
Introduction: A mucocele is a noncancerous abnormality of the mouth that develops when small salivary gland ducts become clogged or when the mouth is traumatized. Due to its many benefits, including less postoperative pain and bleeding and faster recovery, diode laser therapy has grown in popularity. In this particular instance, a 980 nm diode laser was used during a surgical procedure to remove a mucocele from the lower lip.
Case Presentation: The patient was a 23-year-old guy who complained of occasional, painless swelling of the lower lip. Officially, a mucocele was determined. Under local anesthetic, the lesion was removed using a 980 nm diode laser. This procedure allowed for the exact excision of tissue with little damage to adjacent structures. The patient experienced no major side effects or discomfort after the treatment, which indicates that it was well-tolerated. There were no indications of impaired healing during the following appointment.
Conclusion: This case study proves that the 980 nm diode laser is more effective than conventional surgical methods for treating mucoceles. Quick healing, less discomfort, and no incisions are all benefits of the diode laser. It provides a new option for treating oral mucoceles that has shown remarkable improvements in patient outcomes.
Received 15 Mar. 2025; Revised 1 Sept. 2025; Accepted 7 Sept. 2025; Published online 15 Dec. 2025