Evaluation of Nd:YAG Laser Spot Welding for Dissimilar Joining of Nickel and Nickel-Coated Copper in Busbar Lithium-Ion Batteries
Main Article Content
Abstract
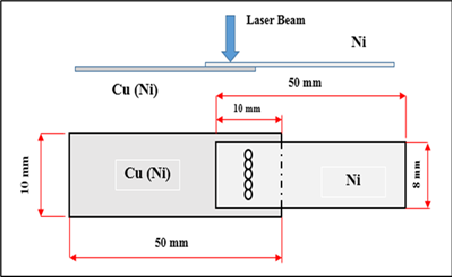
This study aims to evaluate the feasibility of using pulsed Nd:YAG laser spot welding to join dissimilar metals consisting of nickel and nickel-plated copper in busbar joints for lithium-ion batteries. The effects of key operating parameters, namely laser energy, pulse repetition rate, and focal position, on the mechanical and structural properties of the weld were examined. The results showed that an energy of 13 joules achieved the highest peak shear force of approximately 273 N with a homogeneous melt zone and limited surface defects, while an energy of 10 joules recorded the highest hardness value (370HV0.300) due to the balance between energy input and cooling rate. It was also found that a repetition rate of 20 Hz and a focal position at 0 mm represent the optimal conditions for obtaining stable mechanical and microstructural properties. Although the results confirm the possibility of obtaining high-quality welds using this technique, full reliability verification requires further analysis through scanning electron microscopy (SEM), phase analysis (EDS/XRD), and fracture pattern studies to determine failure locations. The study also recommends conducting additional experiments to assess long-term performance under various operating conditions such as vibration, temperature fluctuations, and humidity. Thus, this work contributes a scientific basis that can be relied upon to develop more reliable manufacturing processes in modern battery applications.
Received 17 Jun. 2025; Revised 29 Aug. 2025; Accepted 3 Sept. 2025; Published online 15 Dec. 2025