The clinical evaluation of oral fibroma lesion removal utilizing two types of diode lasers 980 nm and 450 nm
Main Article Content
Abstract
There are a number of advantages to using diode lasers in oral surgery with varying wavelengths. Lasers offer several
advantages, such as reduced recovery periods, the potential to combine tissue coagulation with surgical incisions,
decreased discomfort, field disinfection, and a faster and more efficient healing process. These benefits result in a
decreased reliance on medicine and enhanced patient comfort throughout the recovery phase. This includes a large
AsxzwzA=increase in working efficiency at far lower power settings, among other things. As a result, unwanted
effects can be greatly reduced. It also has a favorable effect on wound healing. The purpose of this study was to
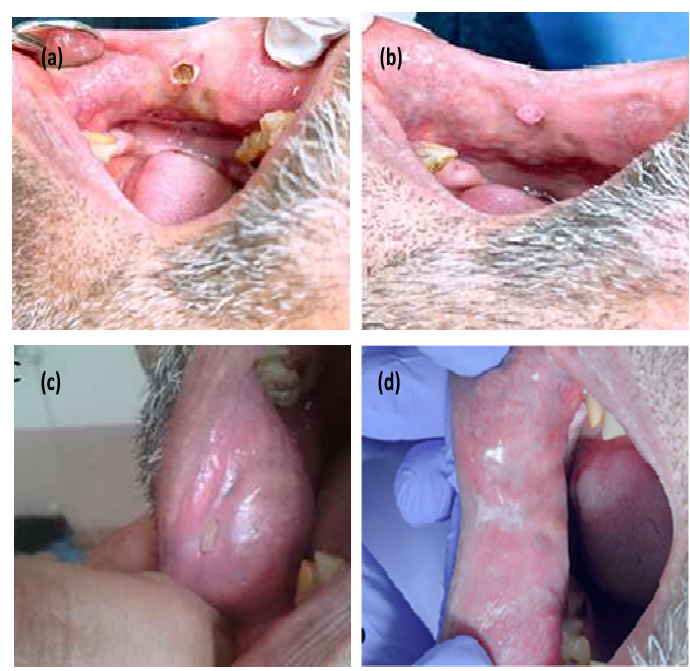
compare two diode lasers (450 and 980nm) to determine whether one is more effective at excision the oral fibroma
lesion with less discomfort, no oedema, and faster healing. In this study, thirty-eight patients between the ages of 16
and 45 were included. The laser parameters setting for both wavelengths were a pulsed wave mode, tip diameter
400µm, and the initial wavelength applied at 1.3 W power. The current study demonstrated that the blue laser with a
wavelength of 450 nm had more efficacy in excising the oral benign lesion. It exhibited reduced discomfort, decreased
swelling, and rapid healing, as observed. The findings of this study indicate that the 450nm diode laser is superior in
effectively eliminating the oral fibroma lesion in a clinical setting while causing minimal patient discomfort and almost
no swelling. In contrast, the 980nm laser resulted in some discomfort and swelling that persisted for a longer duration.
For such instances, the diode laser with a wavelength of 450 nm can be employed with greater effectiveness to
eliminate the oral lesions.
Received 24 Oct.2023; Revised 22 Dec. 2023; Accepted 27 Dec.2023; Published online 15 Jun. 2024
Corresponding Author: [email protected]