Refractive index biosensor based on offset technique of coreless fiber
Main Article Content
Abstract
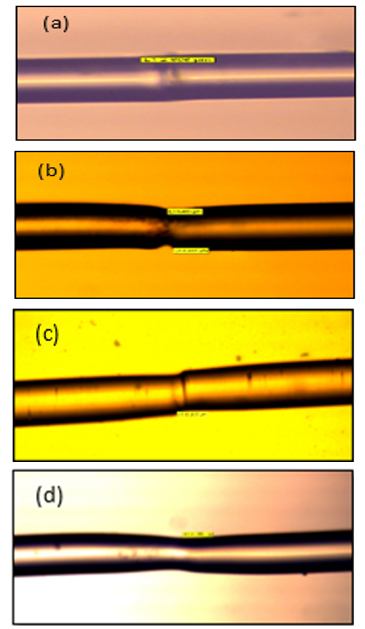
This paper suggested a biosensor structure using an offset technique between two similar coreless fiber
(CF) segments spliced between two single-mode fibers (SMF) for refractive index (RI) measurement of the liquid
pharmaceutical, where experimented with different lengths of CF sections for 10 mm, 15mm, 20 mm, and 25 mm with
different offsets for 2.6 μm, 6.4 μm, and 18.3 μm of symmetric CF sections. This sensor tests different refractive
indices (1, 1.333, 1.337, 1.369, 1.393) of liquid pharmaceuticals The wavelength shifting increases with decreasing
length or displacement of offset. The highest sensitivity was achieved, 255.5 nm/RIU, with the smallest sensor size,
corresponding to the highest refractive index of 1.393 for the Histadin syrup drug, obtained using the optimal length
and offset. This sensor has the capability to detect various refractive indices of chemicals and biochemical liquids.
Advantages of the proposed sensor include high sensitivity, adaptability, enabling faster real-time measurements, ease
of manufacturing and operation, compact size, lightweight design, and low cost.
Received 27 Jul. 2023; Revised 5 Oct. 2023; Accepted 15 Oct. 2023; Published online15 Jun. 2024
Corresponding Author: [email protected]