In vitro study of the antibacterial property of 940 nm diode laser against Streptococcus mutans bacteria isolated from dental caries
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: The main etiological element of dental caries is Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans) bacteria, so getting
rid of this bacterium has a significant impact on how well restorative treatment goes. New approaches for eradicating
bacteria in dentistry have been developed like lasers, metallic nanoparticles, and bioactive materials.
Aim of the study: This study's goal was to assess a diode laser's effectiveness as an antibacterial agent and then
compare it with the antibacterial effect of chlorhexidine (CHX) against S. mutans bacteria.
Material and Method: The study was performed by using S. mutans microorganisms collected from patients with
dental caries, then a bacterial suspension was prepared at a concentration of 106 CFU /ml and placed in an Eppendorf
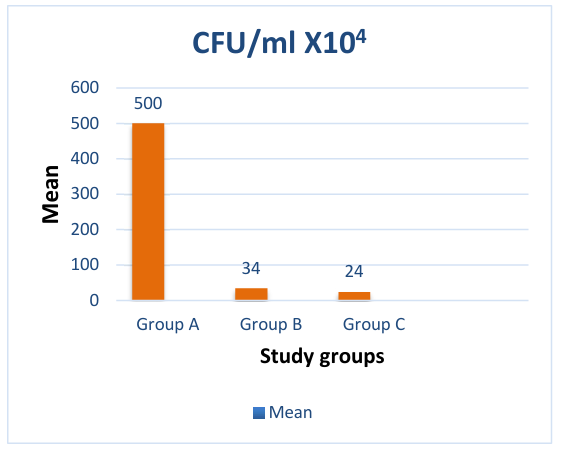
tube to be treated with various antibacterial modalities, the 30 samples were divided up into three experimental groups:
Group I: Negative control group; Group II: Positive control group using 2% chlorhexidine; Group III: Irradiation with
diode laser (1 watt output power for 30s exposure time). The number of colony-forming units (CFU) was counted for
each group after 24 h of incubation on Mitis Salivarius Bacitracin agar (MSBA) plates.
Results: A significant reduction in the CFUs/ml of S. mutans bacteria was observed 24 hours following treatment
by the two approaches (The diode laser and CHX). The findings of the study indicate a significant statistical difference
(p-value < 0.01) between the two groups in comparison to the negative control group that did not receive any treatment.
Furthermore, the group treated with the diode laser exhibited the greatest drop in bacterial count compared to the
group treated with CHX.
Conclusion: Both diode laser and CHX have a good bactericidal effect, but the diode laser had an antibacterial
effect superior to CHX. The diode laser was a successful and effective approach for eliminating bacteria and it can be
employed as a step in the teeth restoration process.
Received 13 Jul. 2023; Revised 27 Oct. 2023; Accepted 4 Nov. 2023; Published online 15 Jun. 2023
Corresponding Author: [email protected]