Comparative evaluative study of Erbium, chromium YSGG and wavelength-dual Diode lasers in oral soft tissue incision morphology: a histological ex vivo study
Main Article Content
Abstract
Laser is an advantageous system that can be used in different medical applications, and one of them is
soft tissue handling in periodontal and surgical dentistry. The recent research aimed to histologically compare the
erbium, chromium YSGG laser, and wavelength-dual diode laser in oral surgical incisions according to cutting
morphology.
Method: This was an ex vivo study using the pieces of tongue from the sheep as samples. 810(50%) + 980 (50%)
nm diode laser was operated continuously (CW) with two average powers: 1.5 and 2.5 W. 2780 nm erbium, chromium
YSGG laser was used in pulse mode with two average powers: 2.5 and 3.5 W. Incisions were made on the tongue
parts, and after histopathological processing, the regularity and morphology of the incision and the cutting depth of
each incision were measured under a light microscope.
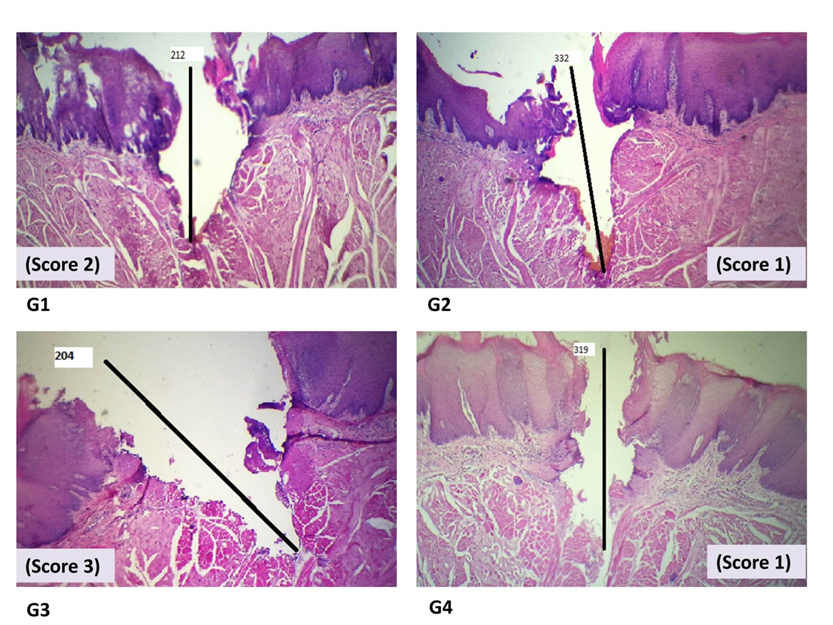
Results: The regularity and morphology of erbium, chromium YSGG laser incisions were significantly higher in
quality (especially those of the low output power of 2.5 W) than those of the diode laser (P value < 0.05). The cutting
depth was significantly higher when the power increased, no matter the type of laser system (P value < 0.05).
Conclusions: Most regular incisions have been achieved with 2.5 W power of Erbium, Chromium YSGG laser.
Received 4 Jan. 2024; Revised 26 Mar. 2024; Accepted 1 Apr. 2024; Published online 15 Jun. 2024
Corresponding Author: [email protected]
Article Details
Issue
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.